Humanoid robot has been present in humankind's imagination for a long time. Nowadays, with the rapid development of science and technology, humanoid robots are becoming reality. Humanoid robotics is currently among the most active branches of robotics research. The potential applications of humanoid robots are infinite: searching and rescuing in catastrophic incidents, working in toxic environments, entertainment, education, and more. Besides that, humanoid robotics research push the boundary of human knowledge in many fields, such as biomechanics, mechanical design, computation, and control.
The HERO project (previously called HURON) aims to create a full-scale, full-body humanoid robot with two main values in mind:
Within this project, we have active research in a variety of fields, including control theory, effective mechanical design, and sensors.
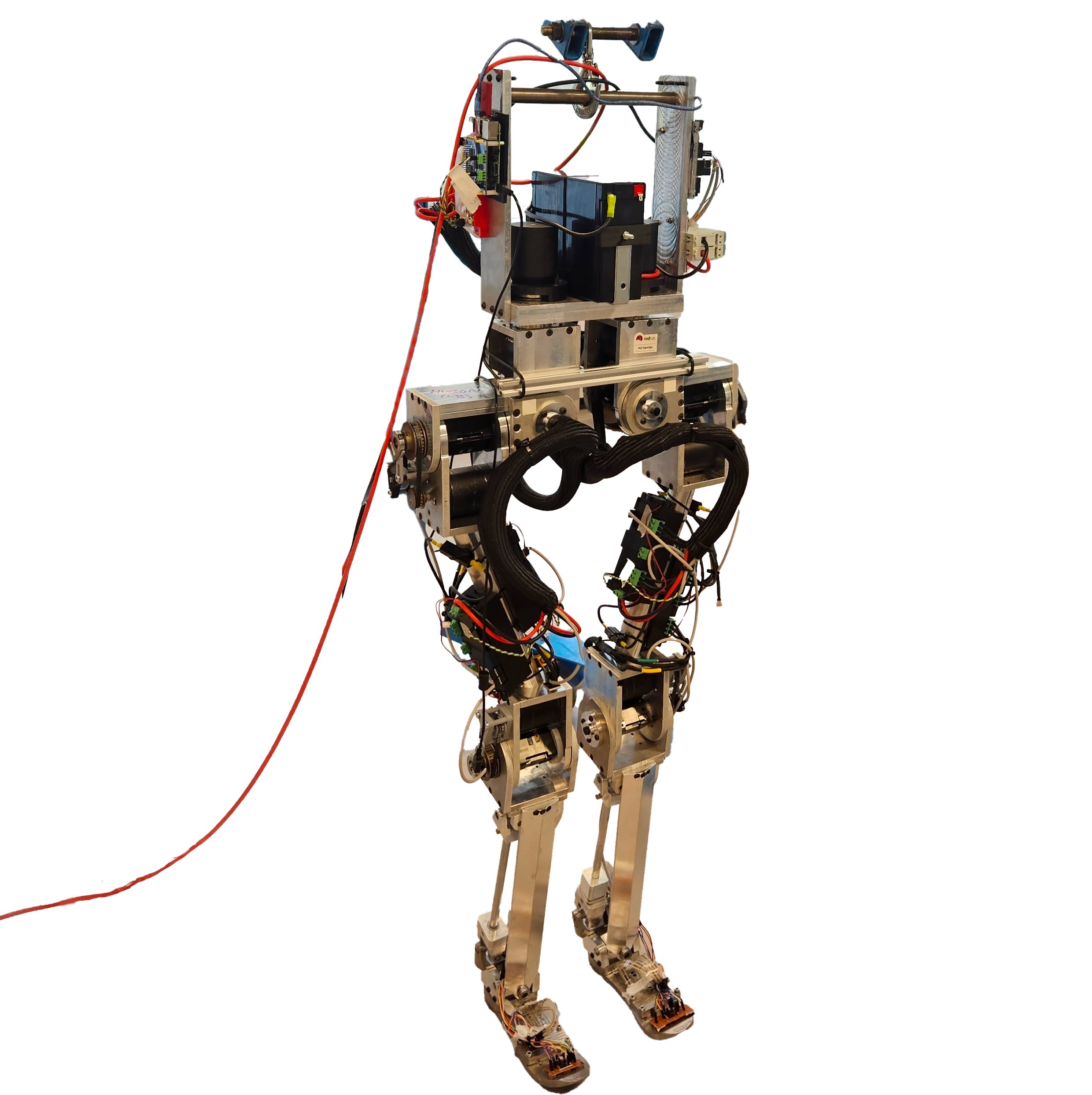
Developing a full-body human-like robot: We have been continuously developing a humanoid robot that resembles human anatomy, is cost-effective, and can serve as a solid platform for applying advanced control algorithms. Currently, we are designing the 3rd version of the ankle joint with the core being the four-bar mechanism and the use of harmonic drives. The goal of this version is to closer match the human leg shape and reduce the cost of materials.
Standing push recovery: The standing push recovery problem occurs when a robot in standing position needs to resist external disturbance without falling down. We propose a new controller based on momentum concepts and a new reaching law for sliding mode control that can help the robot withstand higher forces while standing.
Stepping push recovery: A standing humanoid robot can only withstand a range of external disturbance such that two feet stay flat on the ground. If forces are outside this range, the robot can no longer stand stably. Similar to how human react to forces, the robot needs to take a step to be balanced. This problem is called the stepping push recovery.
Walking on uneven terrain/complex environment: Uneven terrain poses a great challenge for humanoid robots to walk through stably. However, as flat and clean terrain is rare in the real world, humanoid robots need to overcome this problem to be practical.